Projects in Digitalization and Innovation
1. Name of the Assignment: Study/Research: Viability assessment of unmanned aerial system (UAS) services in the context of smallholder wheat and potato farming in Rwanda.
Client: CTA, the University of Rwanda, and Charis Ltd
There is a general consensus that smallholder farming needs to become more productive, more sustainable, and more profitable. Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) or drone-based system services can contribute towards these goals by bringing some of the tools of precision agriculture to producers, which include large and medium-scale holdings and associations of small-scale farmers growing the same crop in contiguous areas. In 2018-19, CTA is upscaling its activities to increase the number of countries covered and the number of UAS operators across Africa and to assess via scientific on-site research, the costs and benefits of the technology. These activities and this project are framed within the larger intervention known as Transforming Africa’s Agriculture: Eyes in the sky, smart techs on the ground.
RCID Ltd, in collaboration with CTA, the University of Rwanda, and Charis Ltd, conducted a comprehensive study from 2017 to 2019 to assess the viability of Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) services in smallholder wheat and potato farming in Musanze District, Rwanda. The study aimed to determine whether smallholder farmers, acting on data-driven advice generated via UAS, could increase their net income through higher yields or reduced costs, such as lower fertilizer use.
The research began with a baseline survey of smallholder farmers cultivating Irish potatoes and wheat in the region. This was followed by extensive training and extension services, which guided farmers from production to harvest, utilizing UAS technology to optimize their practices.
One of the key components of the study was to assess the willingness of individual farmers and farmer cooperatives to pay for UAS advisory services by analyzing a cost-benefit analysis comparing farmers who received UAS-based advisory services with a control group that relied on conventional farming advice. The findings of this study contributed to the broader initiative of transforming African agriculture by integrating advanced technologies like UAS into traditional farming practices. The project not only highlighted the potential of UAS to enhance agricultural productivity but also explored its economic viability, offering valuable lessons for the future of precision agriculture in Rwanda and beyond.




2. Name of the Assignment: Study on Satellite Imagery-Based Crop Monitoring Application in Rwanda.
Client: DFID's Agriculture Technical Assistance Facility (Agri-TAF) at the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI) in Rwanda
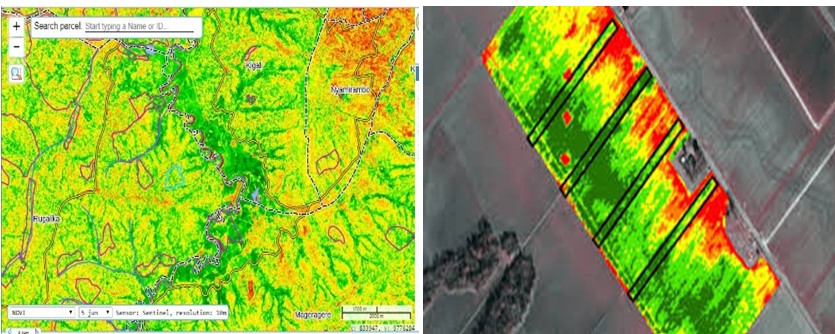
RCID Ltd, supported by DFID's Agriculture Technical Assistance Facility (Agri-TAF) at the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI) in Rwanda, conducted a study to develop a Satellite Imagery-Based Crop Monitoring Application. This project aimed to create a pilot Crop Monitoring System (CMS) for Land Use Consolidated Areas (LUCA) and non-consolidated areas from November 2018 to May 2019. The CMS leverages Sentinel 10x10 meter satellite imagery to monitor changes in the green vegetation index (NDVI) over time, providing valuable insights into crop growth and enabling the analysis of trends in specific areas.
RCID Ltd's primary tasks included validating satellite data and enhancing the interpretation of mapped information. This involved cross-checking the LUCA database against other agricultural lands, verifying cropping areas and types of crops grown through key informant interviews, and gathering data on cropping trends, such as planting times and input usage. The study also focused on identifying factors influencing crop yields in current and previous seasons.
To ensure accuracy, RCID conducted detailed field yield measurements for 155 farmers across six agroecological zones in Rwanda. This comprehensive approach aimed to provide MINAGRI with a robust tool for monitoring crop growth, enabling early warnings and informed decision-making. The pilot CMS developed through this study is a significant step forward in supporting MINAGRI's efforts to track agricultural progress, assess productivity trends, and enhance the overall management of Rwanda's agricultural resources.
3. Name of the Assignment: Agriculture of land use mapping, soil fertility and crop suitability for Bugesera District.
Client: TECAN, funded by the European Union and the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI)
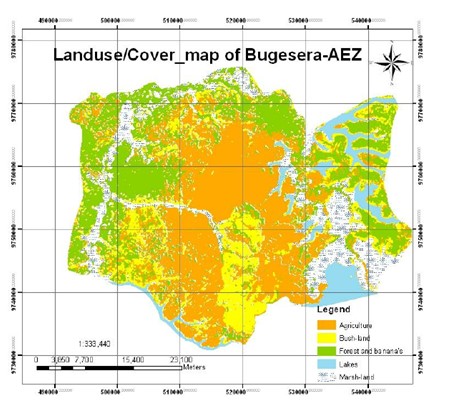
The RCID, in collaboration with TECAN, funded by the European Union and the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI), conducted an extensive study on land use mapping, soil fertility, and crop suitability for Bugesera District between 2021 and 2022. This project aimed to establish a standard methodology for the creation of Agricultural Land Use Zones (ALUZ) as part of the Revised District Land Use Master Plans within the framework of the National Land Use and Development Master Plan (2021–2050).
The study focused on assessing soil fertility to support the implementation of agricultural land zoning in Bugesera District. It identified significant nutrient deficiencies and recommended the use of organic matter and lime to enhance soil health and reduce acidity before fertilizer application. The project also employed advanced image classification techniques to categorize land cover types, including cropland, pasture, forest, and urban areas. By analyzing historical satellite imagery, the study detected changes in land cover over time and assessed their impact on agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
The study utilized Geographic Information System (GIS) tools to conduct spatial analyses, such as modeling crop suitability based on climate, soil, and water availability. Local stakeholders, including farmers and agricultural experts, were actively involved in the planning process to ensure that the spatial planning model was informed by on-the-ground knowledge and preferences. This collaborative approach aimed to optimize land use, enhance agricultural productivity, and promote environmental sustainability in Bugesera District.
Additionally, RCID consultants evaluated water resource availability and management, integrating soil maps and satellite data to assess crop suitability.
Rainwater harvesting and dams in Rwanda
4. Name of the Assignment: Develop cost-sharing models for passive telecommunication base station infrastructure, and fiber optic infrastructure, and develop their related regulatory instruments.
Client: Rwanda Information System Authority (RISA)
RCID Ltd, in partnership with JIDCOM and PROGRESSUS, is undertaking a crucial project to develop cost-sharing models for passive telecommunication base station and fiber optic infrastructure in Rwanda. This initiative, running from July to December 2024, aims to create robust regulatory instruments to support the Rwanda Utilities Regulatory Authority (RURA) in promoting optimal use of telecom infrastructure and enhancing public utilities.
The project focuses on determining the actual costs associated with infrastructure sharing, including towers, electricity, and fiber optics. Sites will be categorized based on tower heights and power access. Various price-setting methodologies will be evaluated, and clear guidelines for co-location will be established, ensuring efficient resource use and encouraging investment in underserved areas.
In addition, an assessment will be conducted to refine cost-sharing models, taking into account market dynamics and public interest. This assessment will also support the modernization of policy, legal, and regulatory frameworks, aiming to improve Rwanda’s telecom sector, including telecommunications, broadcasting, ICT, postal services, energy, water, sanitation, and transport. The ultimate objective is to create a detailed "Requirement Matrix" and recommendations that will guide Rwanda’s telecom sector toward more efficient, sustainable, and equitable use of its infrastructure, fostering growth and development in the process.
RCID Ltd's role in this consortium includes enhancing RURA's ability to engage with stakeholders, analyzing data, reviewing existing policies, and recommending regulatory improvements. The project will also identify gaps and requirements in infrastructure cost-sharing, benchmark models against regional and international standards, and gather stakeholder feedback to ensure successful implementation.

5. Name of the Assignment: Data-driven insight for sustainable agriculture in Africa (DISA) in Rwanda
Client: Future Earth and Quebec Artificial Intelligence Institute (MILA), Canada
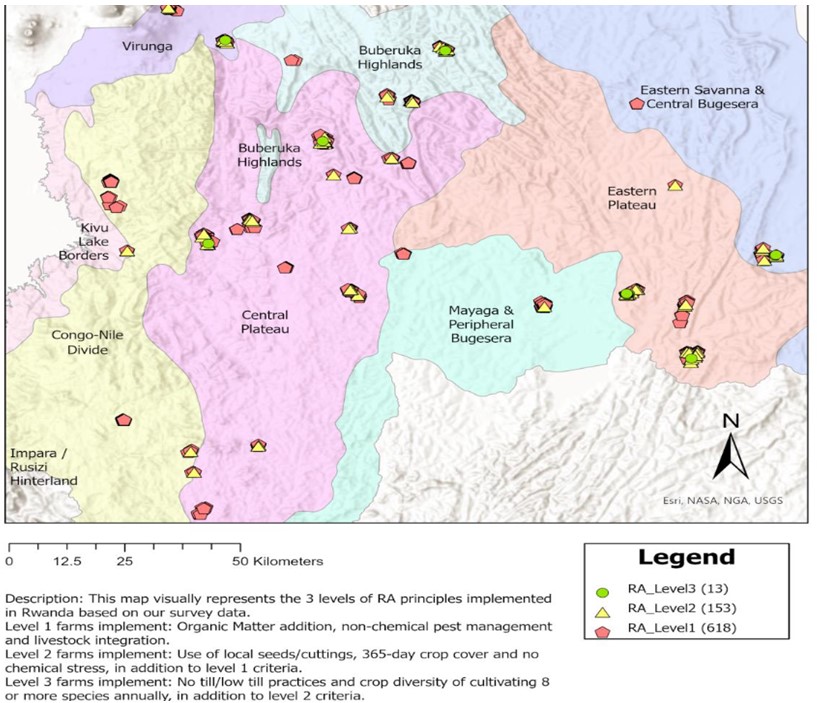
RCID, in partnership with Future Earth under the Sustainability in the Digital Age and the Quebec Artificial Intelligence Institute (MILA), Canada, is conducting a study on Data-driven Insight for Sustainable Agriculture in Africa (DISA) in Rwanda. This project, started in November 2022, aims to empower community-led regenerative agriculture (RA) as a nature-based solution for climate mitigation while enhancing smallholder farmers' capacity to adapt to climate change.
The DISA project explores the role of biodiversity in mediating the effects of RA on the socio-ecological resilience of smallholder farmers at both farm and landscape scales. It also investigates how digital tools, supportive policy frameworks, and South-South knowledge exchange can create enabling conditions for RA adaptation in various contexts.
The project emphasizes the importance of peer-to-peer experiential learning to strengthen capacity development in RA practices, thereby scaling up climate resilience. Advanced technologies such as machine learning algorithms and AI are central to the study. These technologies are used to analyze satellite imagery, detect RA practices at scale, and recommend optimal crop rotation schedules based on historical data. The project also explores the potential of robotics in automating RA practices and assesses the economic feasibility of integrating these systems into farming operations.
Through a survey of 815 smallholder farms across 10 agroecological zones in Rwanda, the study characterizes the adoption of RA practices and assesses their impact on climate mitigation, biodiversity, and socio-economic resilience.