RCID Digitalization Projects & Impact
Explore our pioneering work in GIS, remote sensing, digital agriculture, and smart infrastructure.
10+
Major Projects
5,000+
Beneficiaries
Nationwide
Impact
Agricultural Land Use Mapping, Soil Fertility, and Crop Suitability Analysis in Bugesera District, Rwanda
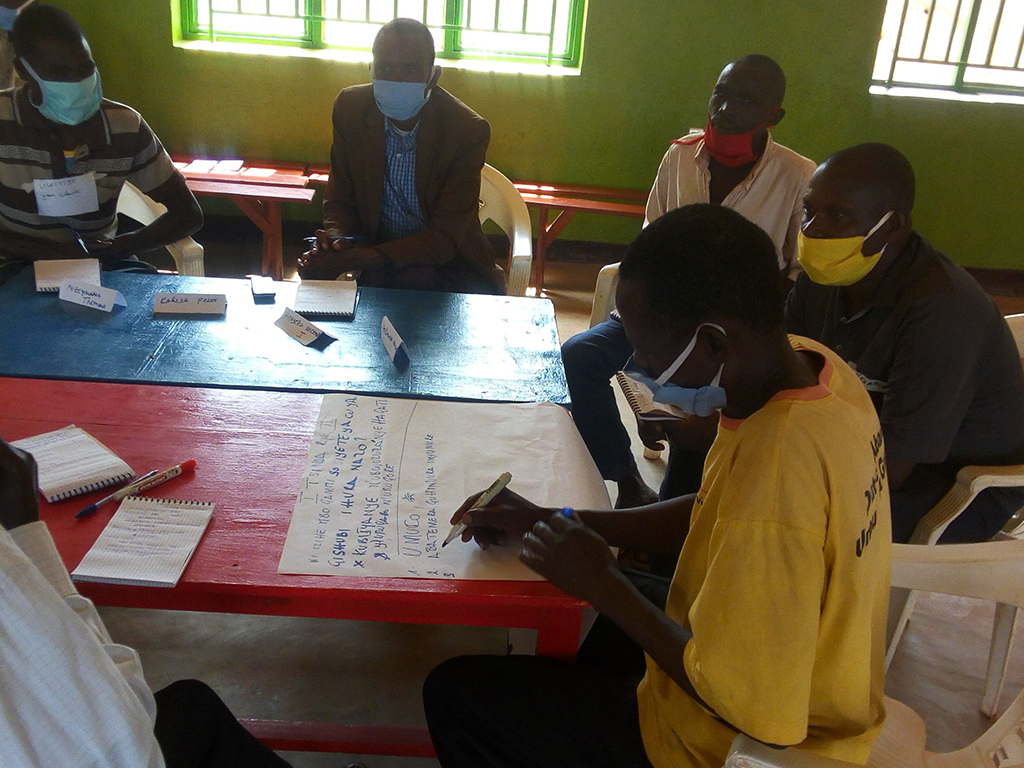
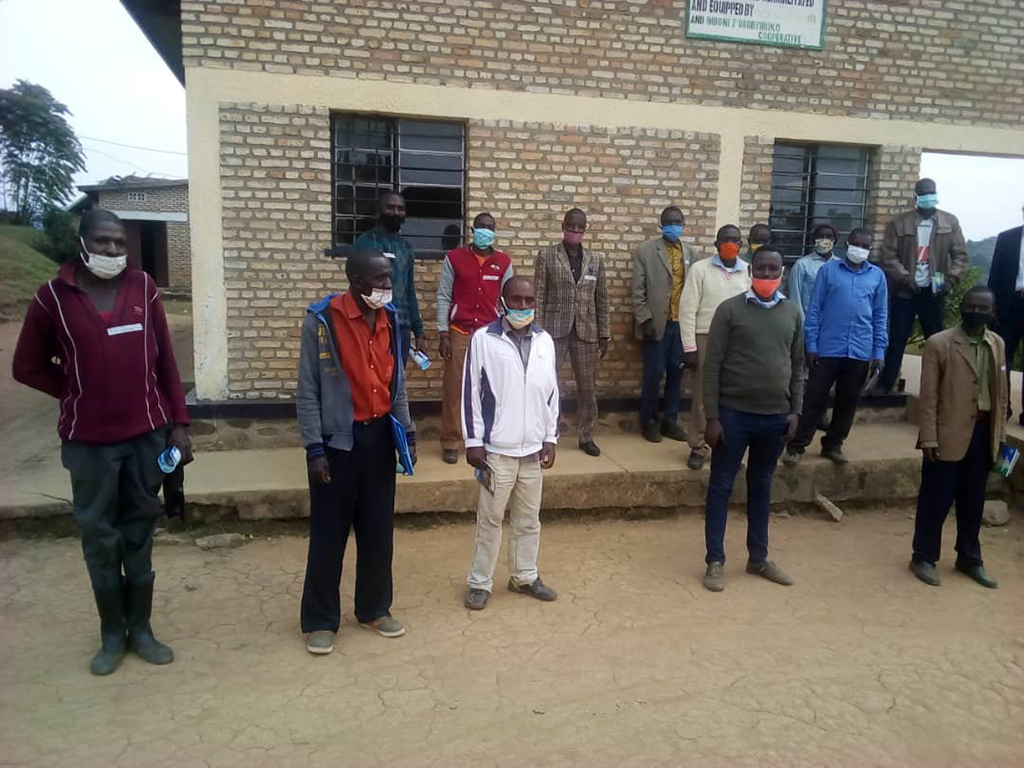
Commissioned by the Assistance to Enhance the Government of Rwanda’s Capacities in the Agriculture Sector for the Sustainable Use of Land and Water Resources, Value Creation and Nutrition Security (TECAN)/MINAGRI) program under the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI), the Regional Research Centre for Integrated Development (RCID) in 2022 conducted a comprehensive study on land use classification, soil fertility, and crop suitability to inform the revision of the Bugesera District Land Use Master Plan. This assignment was part of the broader effort to enhance the Government of Rwanda’s capacity for sustainable land and water resource use, value creation, and nutrition security.
RCID applied a multi-layered approach involving soil sampling, remote sensing, GIS spatial modeling, and community participatory mapping. These activities provided critical technical inputs for zoning agricultural land and guiding sustainable land use planning in alignment with the Rwanda Government. The resulting maps displayed land degradation hotspots, crop suitability zones, and soil health indicators, which are essential for targeting interventions and maximizing land productivity.
Key services provided included land classification, historical land cover change detection, and the analysis of land tenure dynamics. Hydrological modeling was conducted to evaluate water availability and optimize its agricultural use. Soil and crop analysis integrated satellite imagery and soil data to determine nutrient content, moisture levels, and overall crop suitability.
GIS-based spatial analysis and modeling allowed RCID to simulate potential outcomes of various agricultural practices, strengthening local decision-making. The process was highly participatory, engaging farmers, local authorities, and agricultural experts to ensure that scientific recommendations were context-specific and implementable. This project underscores RCID’s leadership in spatial planning, agro-environmental research, and participatory land use development. Visit www.rcid-rwanda.org for more information.
Mapping the Soil fertility status in Bugesera (pH H2O, soil organic carbon, CEC and total nitrogen), under TECAN/MINAGRI program
Mapping the Soil fertility status in Bugesera from left up, right up, left down and right down (pH H2O, soil organic carbon, CEC and total nitrogen), under TECAN/MINAGRI program.
Baseline on satellite Imagery-based Crop Monitoring application in Rwanda
The Regional Research Centre for Integrated Development (RCID Ltd) was contracted by the Agriculture Technical Assistance Facility (Agri-TAF), a UK DFID-funded program under Rwanda’s Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI), to conduct a baseline study on the application of satellite imagery for crop monitoring. The initiative was part of Agri-TAF’s broader support to MINAGRI from 2016 to 2019, aimed at improving evidence-based planning and delivering inclusive agricultural growth for the country’s most vulnerable populations.
The assignment focused on developing a pilot Crop Monitoring System (CMS) to assess agricultural productivity and land use in both Land Use Consolidated Areas (LUCA) and non-consolidated areas. The system was built using Sentinel satellite imagery with a 10x10 meter resolution, tracking changes in the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) to monitor green vegetation cover and seasonal crop growth. The data served as a critical tool for identifying trends over time and space and improving early warning systems related to agricultural performance.
RCID’s role in the study involved interpreting WorldView satellite maps across six districts Gakenke, Gatsibo, Kamonyi, Karongi, Nyaruguru, and Musanze. The team validated satellite-derived data by cross-checking it with field-level information on crop types, planting calendars, input use, and other yield-influencing factors. Field visits and stakeholder consultations ensured that technical data was grounded in practical, local realities.
Additionally, RCID contributed to developing a land use classification algorithm and conducted crop-cutting experiments to further validate remote sensing findings. This work enhanced the government’s capacity to track cropping patterns, assess land degradation, and guide intervention planning. The baseline study demonstrated RCID’s capacity to integrate geospatial technologies with agricultural development, supporting national efforts to modernize crop monitoring and improve decision-making in the agriculture sector.
Study/Research: Viability assessment of unmanned aerial system (UAS) services in the context of smallholder wheat and potato farming in Rwanda
The Regional Research Centre for Integrated Development (RCID Ltd) partnered with the Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation (CTA) in Wageningen, the University of Rwanda, and Charis Ltd to implement a research project assessing the viability of Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) services in the context of smallholder wheat and potato production in Rwanda. This initiative was part of CTA’s broader “Eyes in the Sky, Smart Techs on the Ground” program, co-financed by the European Union, and aimed at transforming African agriculture through digital innovation.
The study was conducted in the Musanze region and focused on whether UAS-based advisory services could increase yields or reduce input costs for smallholder farmers. RCID led the baseline survey and collected data from selected farmers on crop practices, weather patterns, erosion challenges, and input use. Soil and plant sampling protocols were applied to gather data on nutrient levels and crop health, which was then aligned with high-resolution imagery from drone-based mapping to produce diagnostic maps for wheat and Irish potato fields.
These UAS-generated maps provided vegetation indices and crop health indicators that were calibrated with ground-truth data to ensure accuracy. From this, nitrogen prescription maps were developed, allowing for variable-rate fertilizer application tailored to different field zones. The study also analyzed the willingness of individual farmers and cooperatives to pay for such services, comparing results between groups that received UAS-based advice and those using traditional methods.
The findings demonstrated that drone services could provide actionable insights to enhance crop productivity, optimize resource use, and support decision-making at the farm level, offering a promising path for digital agriculture in Rwanda’s high-value crop sectors.
Profiling and Mapping Investments under the Rwanda Dairy Development Project (RDDP)
The Rwanda Dairy Development Project (RDDP) is a six-year (2018 to 2024) initiative implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI), co-financed by the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD). the Government of Rwanda. The primary objective was to promote pro-poor economic growth and enhance rural livelihoods by building a sustainable, inclusive, and climate-resilient dairy value chain that improves food security, nutrition, and economic empowerment of women and youth.
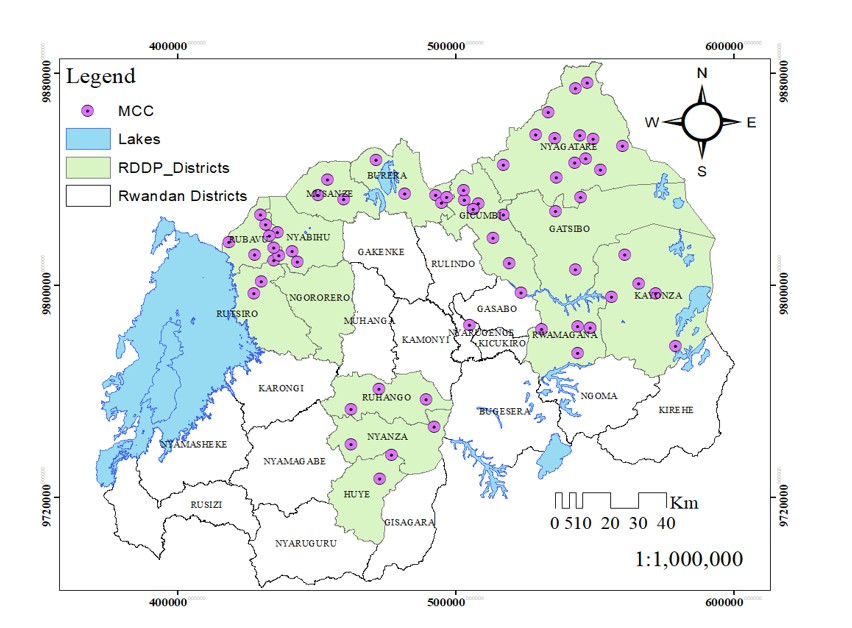
In 2023, RCID was commissioned to support RDDP by profiling and mapping dairy infrastructure investments across 13 districts. Using ArcGIS tools, RCID created a comprehensive offline geodatabase and an interactive online dashboard capturing detailed information on infrastructure location, usage, and beneficiary demographics, including gender, youth, and female-headed households.
RCID’s geospatial work across 13 districts by mapping and profiling 1,154 infrastructures including communal cowsheds, Milk Collection Points (MCPs), Milk Collection Centers (MCCs), boreholes, nitrogen plants, milk zones, and other key infrastructure. The team integrated spatial relationships, usage patterns, and satisfaction levels of service beneficiaries into the analysis.
The findings offer strategic insights for MINAGRI and stakeholders, enabling data-driven planning aligned with the Livestock Master Plan and PSTA4. The project supports sustainable dairy sector investment planning and enhances Rwanda’s capacity to coordinate interventions through a robust, participatory, and evidence-based approach.

"RCID's digitalization projects have empowered Rwandan institutions and communities with data-driven solutions, GIS, and smart infrastructure. Their expertise is shaping Rwanda's digital future."